
Understanding ESG Management and Evaluation Methodologies
- Boreum Lee, Ph.D.
- ESG
- May 25, 2025
What is ESG Management?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance, representing the core indicators for evaluating corporate sustainable management. Unlike the past when companies solely pursued financial performance, modern enterprises are now seeking long-term value creation through environmental protection, social responsibility, and transparent governance structures.

The Importance of ESG Evaluation
Globally, close to 16,000 public and private companies are subject to ESG evaluation, with ESG scores available for approximately 14,500 public entities, significantly influencing decision-making processes of investors, customers, and society at large. Particularly, the LSEG (London Stock Exchange Group) ESG evaluation system provides objective and transparent assessments utilizing over 800 different ESG metrics.
1. Ten Core Evaluation Categories
LSEG ESG evaluation consists of the following 10 categories:
Environmental Pillar:
- Resource Use: Efficiency in materials, energy, and water usage
- Emissions: Management of environmental emissions during production processes
- Innovation: Development of eco-friendly technologies and products
Social Pillar:
- Workforce: Job satisfaction, safe working environments, diversity and equality
- Human Rights: Compliance with fundamental human rights conventions
- Community: Sound corporate ethics and social responsibility
- Product Responsibility: Customer health and safety, data protection
Governance Pillar:
- Management: Transparent and efficient corporate governance
- Shareholders: Protection of shareholder rights and fair treatment
- CSR Strategy: Systematic social responsibility management strategy
2. Scientific Score Calculation Methodology
LSEG ESG scores are calculated through the following five steps:
Step 1: ESG Category Score Calculation
- Separate processing of Boolean data (yes/no) and numerical data
- Relative performance comparison within the same industry group
Step 2: Materiality Matrix
- Weight assignment of 1-10 points for specific ESG elements by industry
- Reflection of data transparency and industry-specific characteristics
Step 3: Overall ESG Score and Pillar Score Calculation
- Derivation of final scores by integrating weighted category scores
Step 4: Controversies Score Calculation
- Reflection of corporate negative issues based on 23 ESG controversy items
- Application of severity weights to reduce market capitalization bias
Step 5: Final ESGC Score Calculation
- Comprehensive evaluation combining ESG scores and controversy scores
3. Grading System and Benchmarking
LSEG provides scores between 0-100 points along with detailed grades from D- to A+:
- A+ (92-100 points): Excellent relative ESG performance and high transparency
- A (83-92 points): Excellent relative ESG performance
- A- (75-83 points): Excellent relative ESG performance
- B+ (67-75 points): Good relative ESG performance and above-average transparency
- B (58-67 points): Good relative ESG performance
- B- (50-58 points): Good relative ESG performance
- C+ (42-50 points): Satisfactory relative ESG performance and moderate transparency
- C (33-42 points): Satisfactory relative ESG performance
- C- (25-33 points): Satisfactory relative ESG performance
- D+ (17-25 points): Poor relative ESG performance and insufficient transparency
- D (8-17 points): Poor relative ESG performance
- D- (0-8 points): Poor relative ESG performance
ESG Evaluation Status of Major Companies
Comparing scores from various rating agencies reveals interesting patterns (note: specific scores may vary as ratings are updated regularly):
| Company | LSEG Score* | S&P Global Score | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | High B range | 50 | Strong in environment and governance |
| Sony | High A range | 55 | Balanced performance across all areas |
| Samsung | High B range | 57 | Strong social and community focus |
*Exact LSEG scores are proprietary and subject to regular updates
These differences stem from varying methodologies and focus areas of each rating agency.
Future Prospects of ESG Management
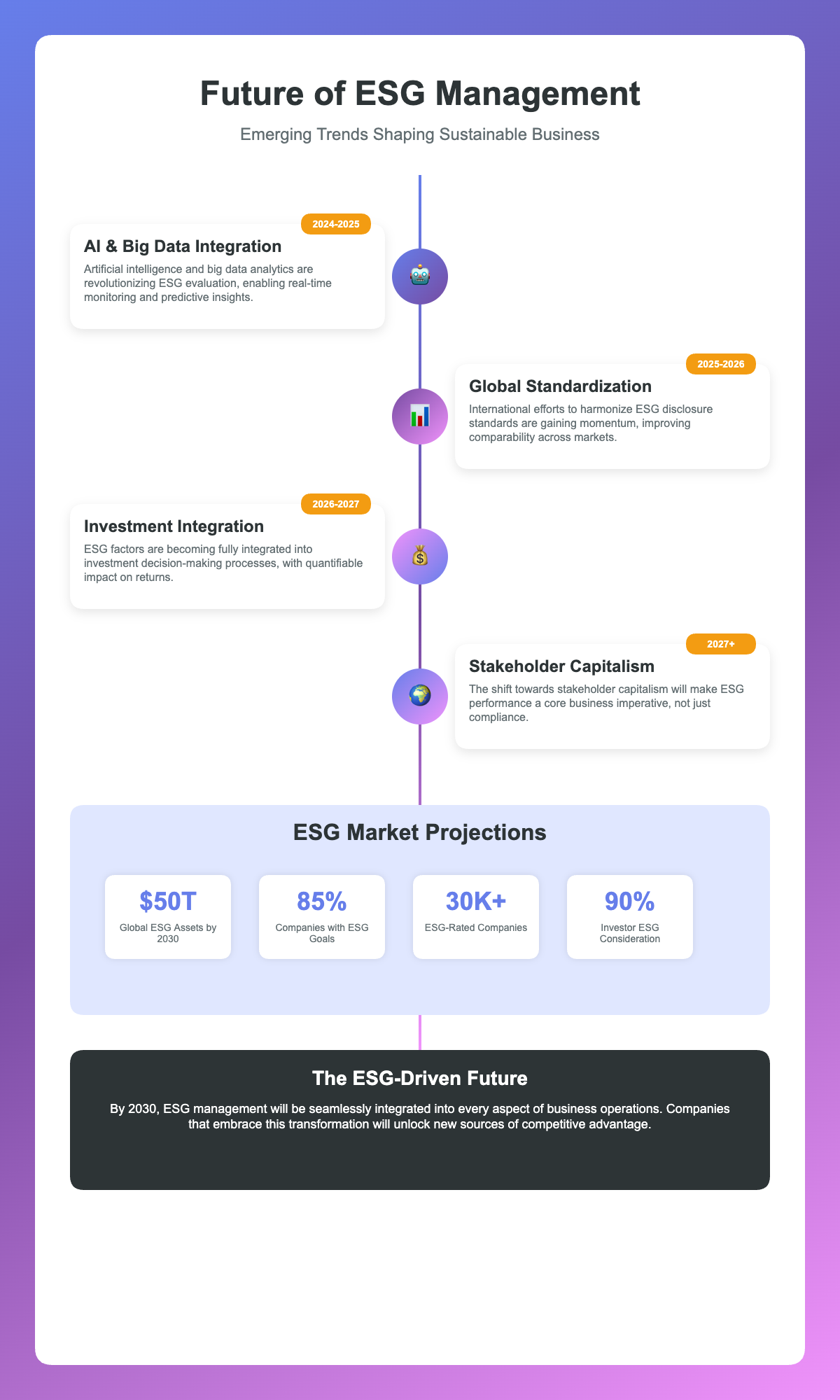
ESG management is evolving beyond simple evaluation in the following directions:
- AI and Big Data Utilization: Real-time ESG data analysis through AI technology, as seen in LSEG and Microsoft’s partnership
- Standardization Progress: Enhanced comparability through integrated global disclosure standards
- Investment Decision Integration: Advanced analysis of ESG factors’ impact on investment returns
ESG Status of Korean Companies
According to Korea ESG Standards Institute evaluation, major Korean companies’ 2023 ESG grades are as follows:
- Samsung Electronics: A Grade (Environment A, Social A+, Governance B+)
- LG Electronics: A Grade (Environment A+, Social A, Governance A)
- Hyundai Motor: A Grade (Environment A, Social A, Governance B+)
This demonstrates that Korean companies are achieving significant results in ESG management.
Conclusion: Strategic Approach to ESG Management
ESG management is no longer optional but essential. Companies need the following strategic approaches:
- Systematic Data Management: Building systems to effectively manage over 630 data points
- Industry-Specific Reflection: Understanding each industry’s materiality matrix and focusing on key areas
- Integrated Perspective: Approaching environment, social, and governance as interconnected systems rather than separate elements
- Continuous Improvement: Ongoing performance enhancement through regular evaluation and benchmarking
ESG management is not a short-term cost but a core driver of long-term value creation. By understanding and utilizing transparent and scientific evaluation systems, companies can simultaneously achieve sustainable growth and social value creation.
This article is based on the LSEG ESG Scoring methodology. For more detailed information, please visit the LSEG official website.
Share :
Related Posts

RE100: The Global Initiative Driving Corporate Renewable Energy Transition
Introduction As climate change response emerges as a global imperative, corporate renewable energy transition is accelerating worldwide. At the center of this movement is RE100 (Renewable Energy 100%). Beyond being an environmental campaign, RE100 has established itself as a core strategy determining corporate competitiveness and sustainability.
Read More
The Importance of Setting the System Boundary for Life Cycle Assessment
What is Life Cycle Assessment? Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a structured process that comprehensively evaluates the environmental impacts of a product or service by collecting and analyzing all material and energy flows within a defined system boundary.
Read More
Getting Started with LCA and SimaPro
Introduction to Life Cycle Assessment I studied Life Cycle Assessment through the “Life Cycle Assessment Student Handbook” (2015). The first section, which provides an overview of Life Cycle Assessment, highlights two key requirements for performing an Life Cycle Assessment:
Read More