
RE100: The Global Initiative Driving Corporate Renewable Energy Transition
- Boreum Lee, Ph.D.
- RE100
- May 23, 2025
Introduction
As climate change response emerges as a global imperative, corporate renewable energy transition is accelerating worldwide. At the center of this movement is RE100 (Renewable Energy 100%). Beyond being an environmental campaign, RE100 has established itself as a core strategy determining corporate competitiveness and sustainability.
What is RE100?
RE100 is a global corporate initiative where companies pledge to source 100% of their electricity from renewable energy by 2050. Launched jointly by Climate Group and CDP in 2014, this campaign has grown into a massive movement with over 400 participating companies worldwide.
Renewable Energy Sources Recognized by RE100
- Wind
- Solar (thermal/photovoltaic)
- Geothermal
- Sustainable Biomass (including biogas)
- Sustainable Hydropower
South Korea’s RE100 Status: Challenges and Opportunities
Domestic Participation Overview
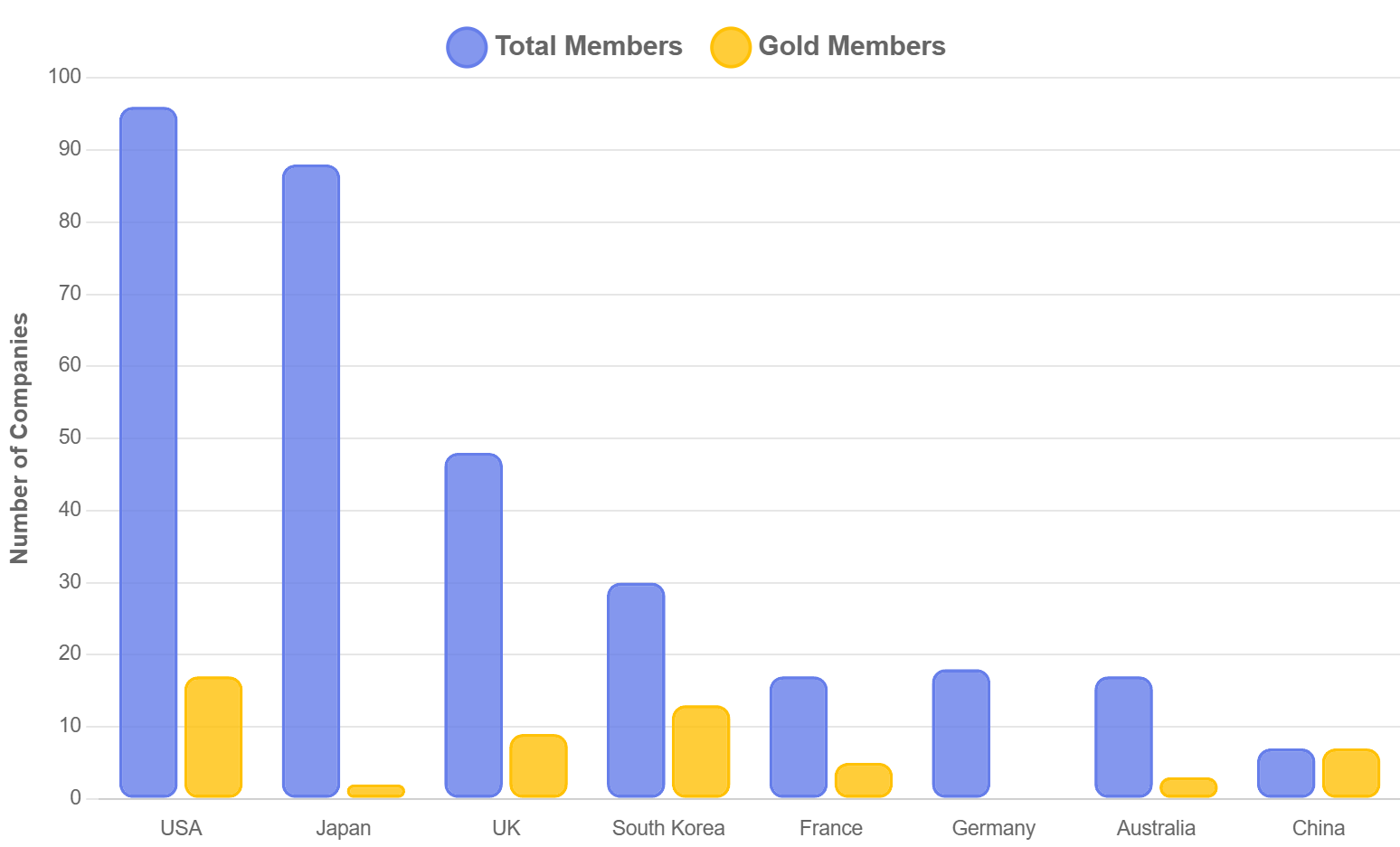
Currently, over 30 Korean companies have joined RE100, with 13 serving as Gold Members. Major conglomerates including Samsung Electronics, LG Energy Solution, SK Telecom, and Hyundai are participating, demonstrating high interest from Korea’s industrial sector.
Key Participating Companies and Target Years:
- LG Energy Solution: 2030
- LG Innotek: 2030
- Kia: 2040
- Hyundai: 2045
- Samsung Electronics, Samsung SDI, SK Telecom: 2050
Challenges Facing South Korea
South Korea is classified as a “challenging market for renewable electricity procurement” for RE100 participating companies. Members source only 9% of their electricity from renewables in South Korea, compared to the global average of 50%. The reasons include:
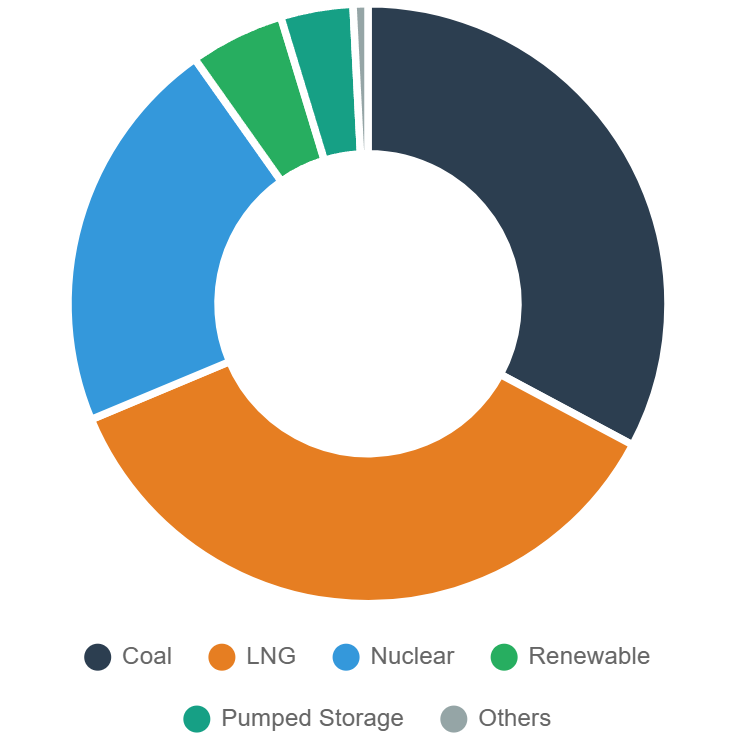
- Low Renewable Energy Share: Wind and solar generation accounts for only 5.4%, with total renewable energy comprising 9% - less than 50% of the global average
- Target Achievement Difficulties: The 2030 renewable energy target was revised downward from 30.2% to 21.6%
- Limited Procurement Options: Direct PPAs, REC purchases, and other options remain restricted
Global RE100 Status: Success Stories
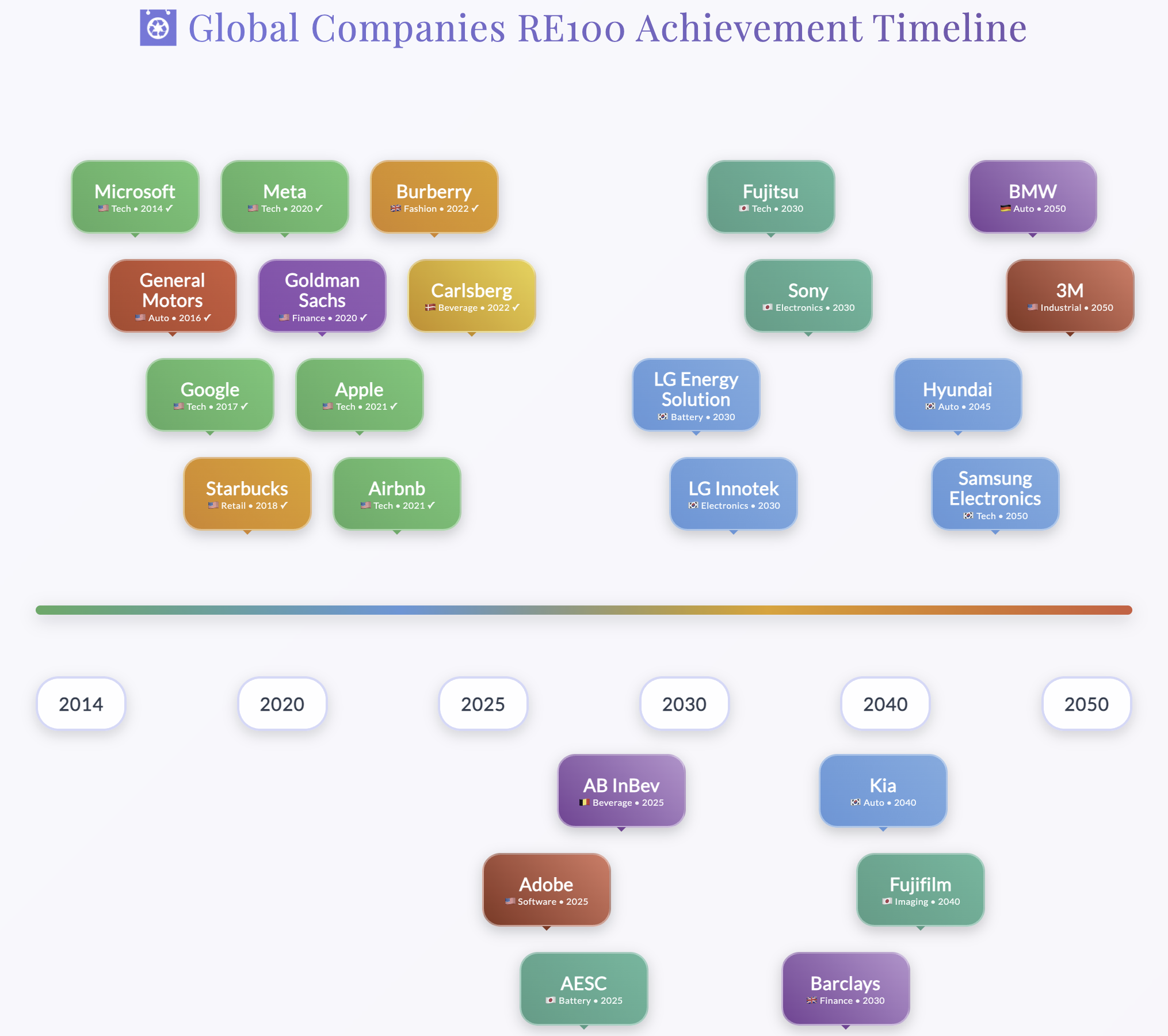
Leading Cases in the United States
California tech companies are presenting successful RE100 models:
- Google: Achieved RE100 in 2017
- Meta: Achieved RE100 in 2020
- Apple: Achieved RE100 in 2021
- Microsoft: Achieved RE100 in 2014
Europe’s Systematic Approach
European companies systematically manage renewable energy certification through the REGO (Renewable Energy Guarantees of Origin) system:
- Burberry: Achieved RE100 in 2022
- Kering: Achieved RE100 in 2022
Asia’s Rapid Growth
- China: 7 companies participating, all Gold Members
- Japan: 88 companies participating; Fujitsu moved its target forward from 2050 to 2030
Procurement Methods for RE100 Achievement
1. Direct Generation
Companies own and operate renewable energy power plants directly
2. Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs)
- Physical PPA: Purchase both actual electricity and RECs together
- Virtual PPA (VPPA): Purchase only the renewable energy ‘value’ without physical power supply
3. Certificate Purchases
- South Korea: REC (Renewable Energy Certificate) system
- United States: REC system
- Europe: REGO/GoO (Guarantees of Origin) system
Economic Impact: Connection with Carbon Pricing
RE100 participation extends beyond environmental purposes to serve as an economic risk management strategy.
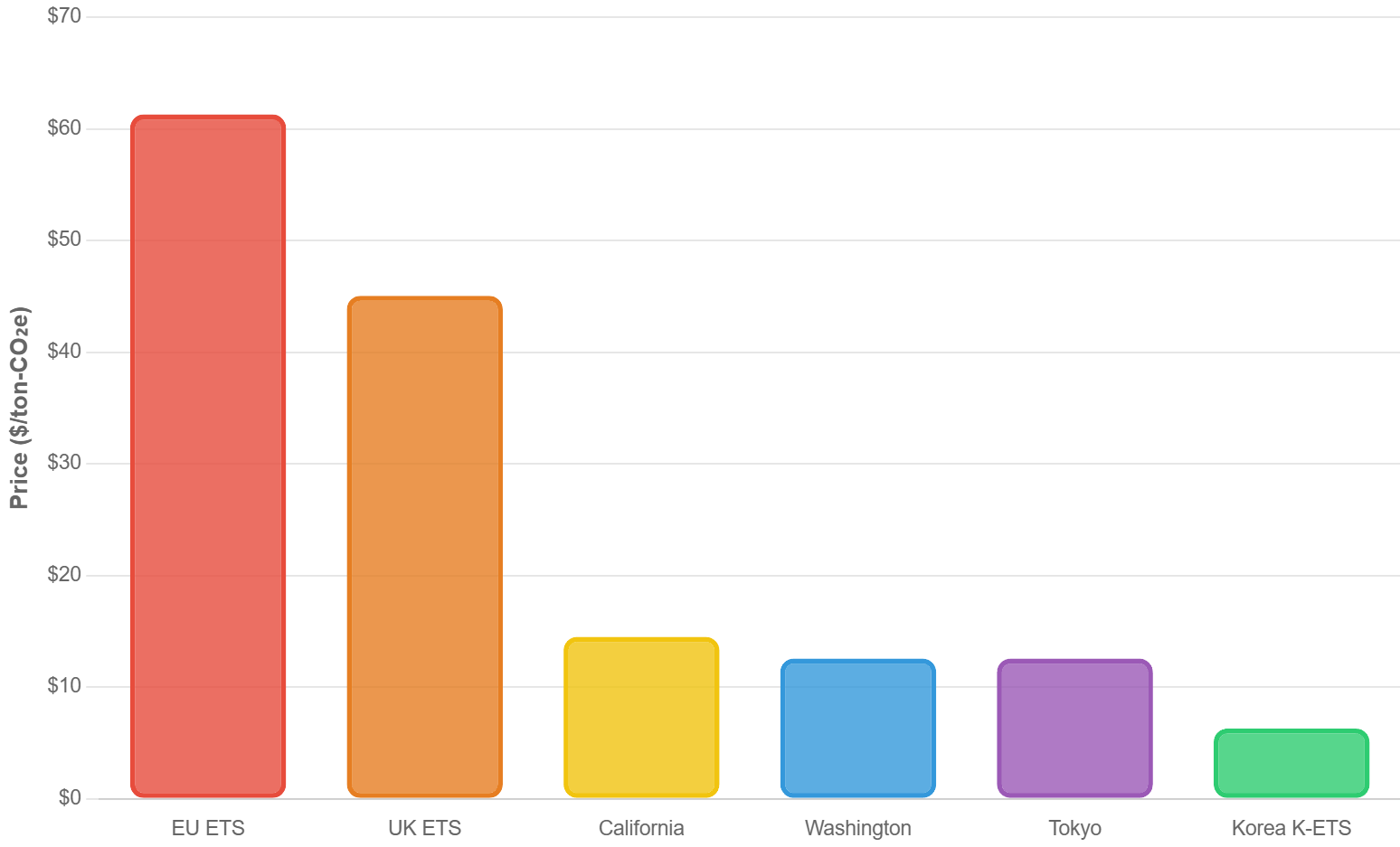
Carbon Price Comparison ($/ton-CO₂e)
- EU ETS: $61.3
- UK ETS: $45.06
- Korea K-ETS: $6.3
Impact on Electricity Prices:
- EU: 20-27% increase over existing electricity prices
- UK: 16-22% increase
- South Korea: 2-4% increase
Considering this upward trend in carbon pricing, RE100 participation serves as a long-term energy cost stabilization strategy.
RE100 Membership Requirements and Benefits
Membership Requirements
- Minimum Electricity Consumption: 0.1TWh/year or more
- Influence: Companies with influence in their region or sector
- Policy Support: Companies supporting RE100-related policies
- Global Impact: Companies with worldwide influence
- Real Economy: Companies producing actual products
Excluded Sectors
Fossil fuel, airline, defense, gambling, and tobacco industries are ineligible
Membership Benefits
- Gold Member (Annual fee $18,000): Access to RE100 events and webinars
- Standard Member (Annual fee $6,000): Basic membership
Reporting and Assessment through CDP
RE100 participating companies must annually report the following through the CDP (Carbon Disclosure Project) questionnaire:
Key Reporting Items
- Energy Consumption (in MWh)
- Renewable Energy Procurement Methods details
- Country-specific Renewable Energy Purchase Status
- Plans for Target Achievement
- Obstacles and Challenges Faced
Future Outlook and Technical Criteria Changes
New Standards for Co-firing Generation
RE100 plans to apply stricter standards for co-firing of fossil fuels and renewable energy. This is due to concerns that co-firing coal with biomass may actually result in higher lifecycle emissions.
Mandatory Use of EACs (Energy Attribute Certificates)
For standardized and transparent renewable energy certification, the criteria are evolving toward mandatory EAC use in markets where EACs are available.
Conclusion: What RE100 Means for Companies
RE100 is not merely an environmental campaign. It represents a strategic choice determining corporate future competitiveness.
Core Values of RE100 Participation:
- Risk Management: Proactive response to carbon price increases
- Brand Value: Building consumer and investor trust in sustainability
- Supply Chain Innovation: Securing competitive advantages in global supply chains
- Long-term Cost Reduction: Leveraging the declining cost trend of renewable energy
For Korean companies, RE100 presents both challenges and opportunities. With government improvements in renewable energy policies and active corporate participation, South Korea can establish itself as a key player in the global RE100 movement.
This article is based on official RE100 materials from Climate Group and CDP. For the latest information, please visit the official RE100 website.
Tags :
Share :
Related Posts

Understanding Carbon Pricing: An Effective Strategy for Greenhouse Gas Reduction
What is Carbon Pricing? Carbon pricing stands as one of the most efficient policy mechanisms for addressing climate change, creating economic incentives for greenhouse gas reduction by assigning a tangible cost to emissions.
Read More
The Importance of Setting the System Boundary for Life Cycle Assessment
What is Life Cycle Assessment? Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a structured process that comprehensively evaluates the environmental impacts of a product or service by collecting and analyzing all material and energy flows within a defined system boundary.
Read More
Understanding Scope-Based Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Introduction Carbon neutrality refers to the process of minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and their sources from human activities, while removing already emitted greenhouse gases through methods such as forest absorption or carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS).
Read More