
Understanding Carbon Pricing: An Effective Strategy for Greenhouse Gas Reduction
- Boreum Lee, Ph.D.
- LCA , Carbon Pricing
- May 14, 2025
What is Carbon Pricing?
Carbon pricing stands as one of the most efficient policy mechanisms for addressing climate change, creating economic incentives for greenhouse gas reduction by assigning a tangible cost to emissions.
Notably, the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism exemplifies how carbon pricing influence can extend into international trade, pioneering new frontiers in global carbon reduction efforts.
Global Carbon Pricing Monitoring System
The World Bank provides transparent global carbon pricing data through its Carbon Pricing Dashboard.
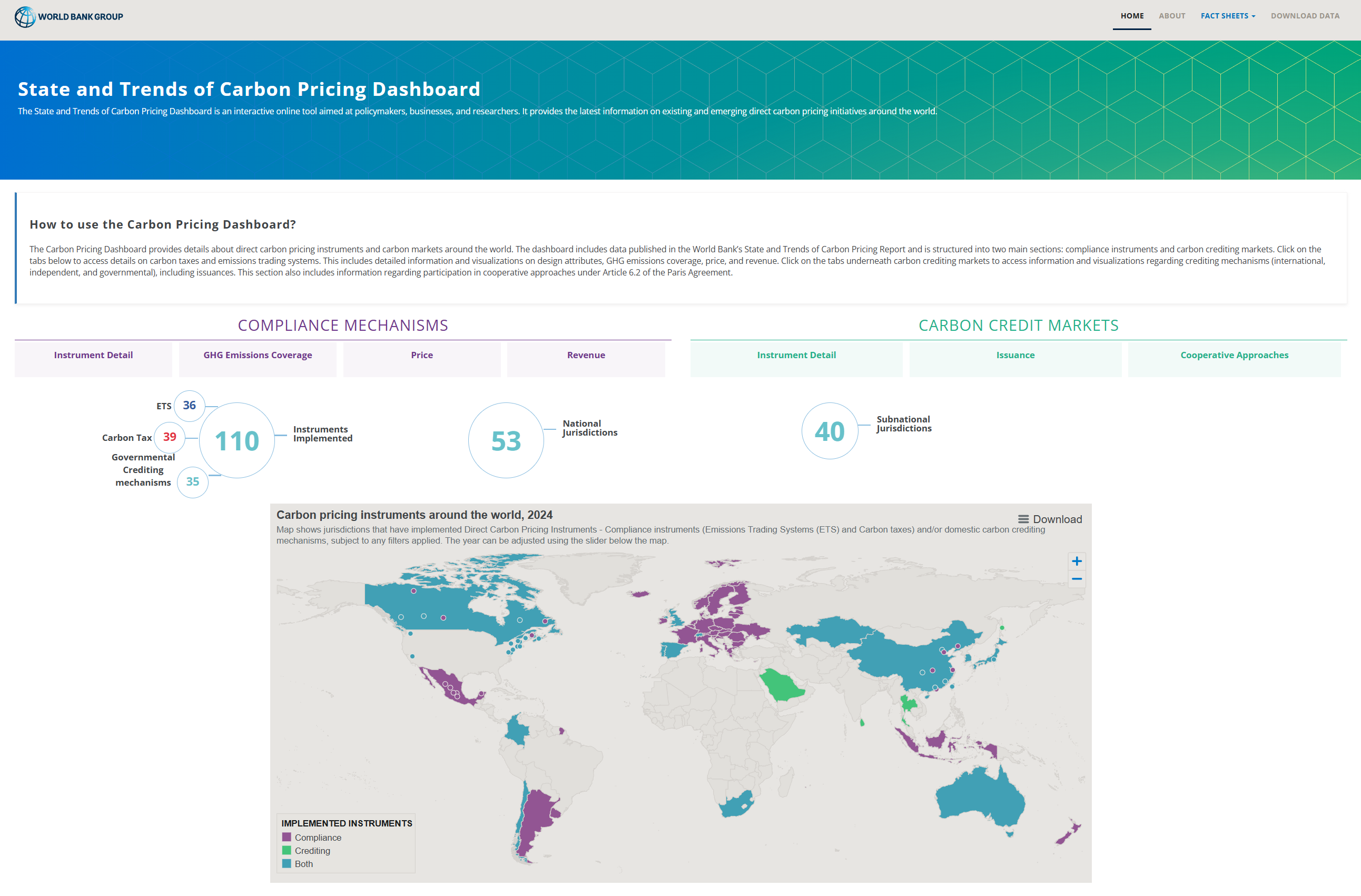
This comprehensive platform details direct carbon pricing instruments and carbon markets worldwide, serving as an essential resource for tracking the evolution of carbon policies across different jurisdictions.
Classification of Carbon Pricing Implementation Stages
Carbon pricing initiatives are systematically categorized as follows:
- Implemented: Fully established legal frameworks with compliance obligations in effect for regulated entities
- Under Development: Active government preparation for specific carbon pricing instruments, officially confirmed through formal channels
- Under Consideration: Official government announcements of intention to implement carbon pricing mechanisms
- Abolished: Previously implemented systems that have been discontinued
Carbon Tax vs. Emissions Trading Systems: Comparative Analysis
Carbon pricing predominantly takes the form of either carbon taxes or emissions trading systems (ETS), each with distinct characteristics and advantages:
| Characteristic | Carbon Tax | Emissions Trading System (ETS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consumption tax imposed on carbon emissions from fossil fuels during production processes | Market-based system allowing entities exceeding emission limits to purchase allowances from those with surplus capacity |
| Economic Efficiency | Effective at minimizing greenhouse gas reduction costs | Optimal resource allocation through market mechanisms |
| Technological Innovation | Promotes development of low-carbon technologies | Incentivizes investment in emission reduction technologies |
| Equity | Burden levels determined by revenue redistribution methods | Participant burdens vary based on allowance allocation and auction revenue distribution |
| Price Equity | Challenges in establishing appropriate tax rates | Easier to achieve price equity through market-based pricing |
| Policy Acceptance | Potential for tax resistance and industry opposition | Requires stakeholder coordination on allowance allocation and reduction targets |
| International Linkage | Requires intergovernmental agreements | Direct linkage possible with other national systems |
Historical Development of Carbon Pricing
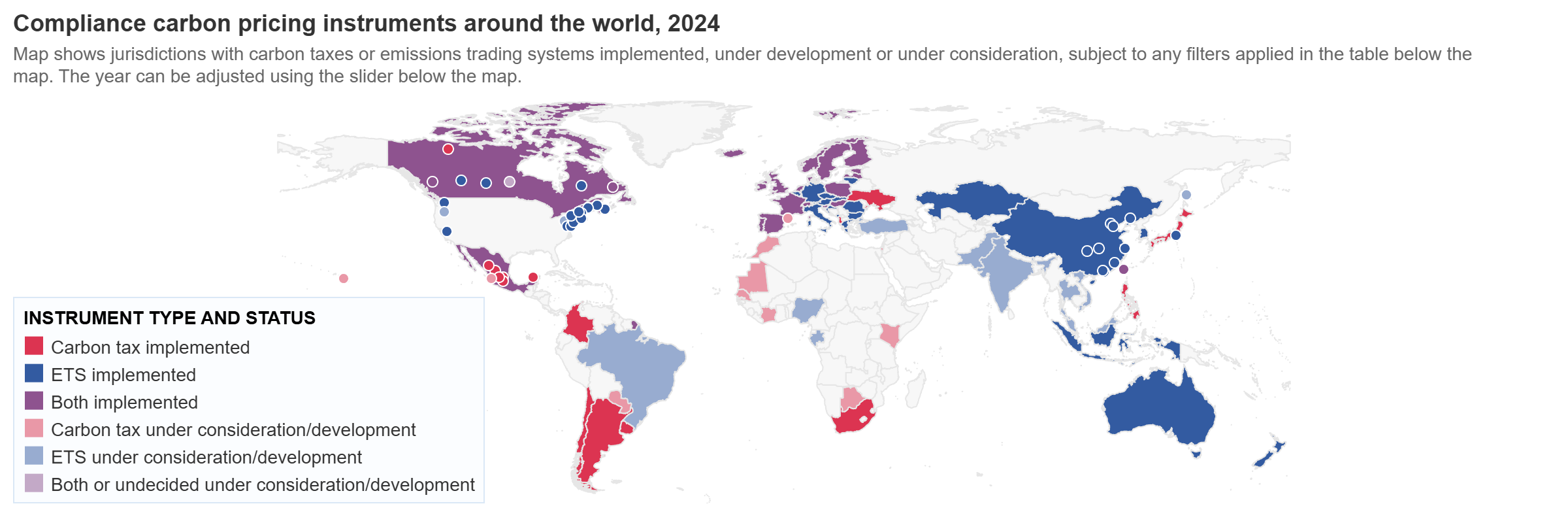
Data analysis reveals that pioneering countries implementing carbon pricing in the 1990s included Poland, Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Slovenia, primarily adopting carbon tax approaches. Poland notably stands as the first country to implement carbon pricing in 1990.
The Emissions Trading System model was first introduced by the European Union in 2005, with New Zealand and Switzerland adopting similar frameworks in 2008, establishing the foundation for global expansion.
Current Carbon Pricing by Country
The World Bank platform systematically tracks carbon prices (US$/tonCO₂e) by country, allowing for analysis of year-over-year price trends.
This data serves as a critical indicator reflecting each nation’s climate mitigation commitment and economic conditions.
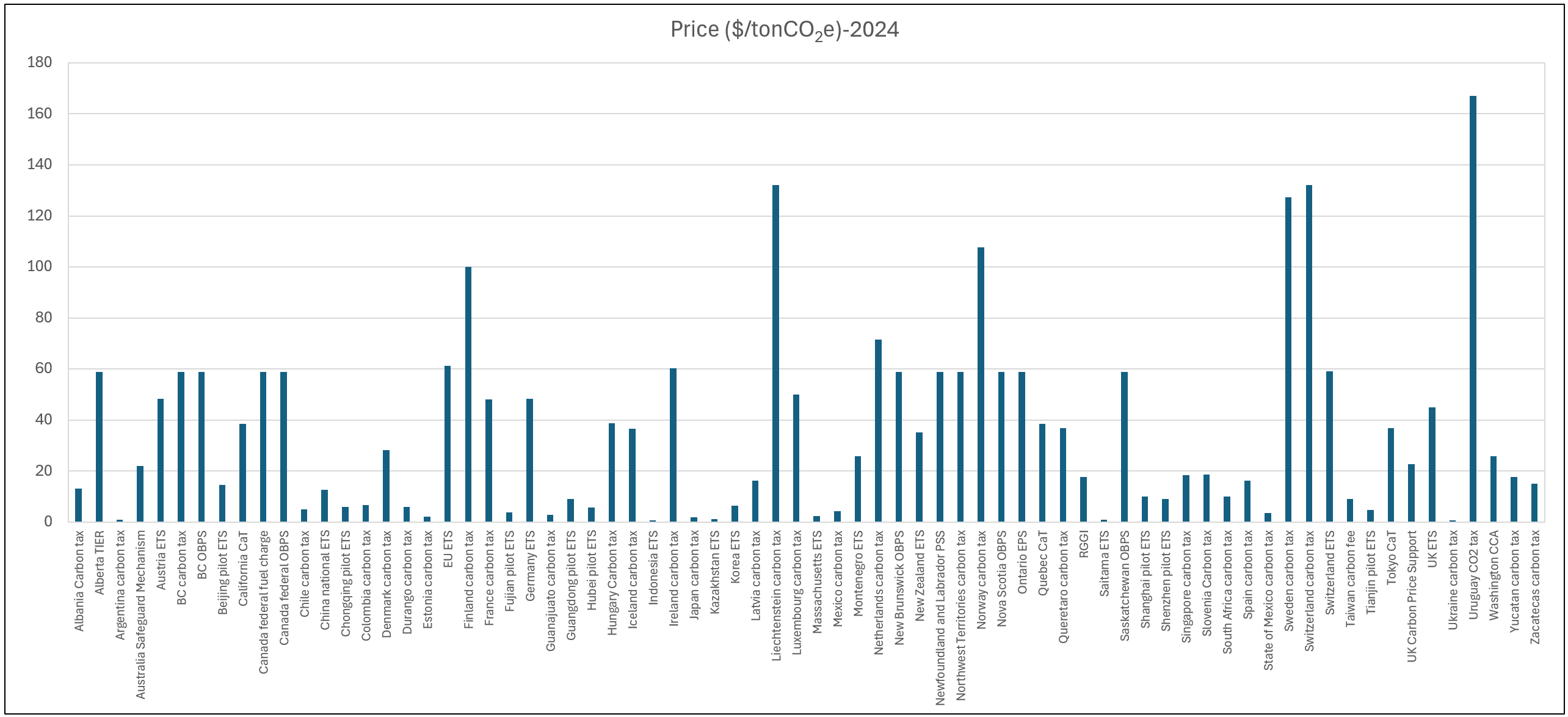
Latest Carbon Pricing Data: Three-Year Global Trends
To support your in-depth analysis, we have compiled comprehensive carbon pricing data from 2022 through 2024 from the World Bank platform into a consolidated Excel file.
This dataset provides at-a-glance visibility into carbon tax and emissions trading system price trends across countries, serving as a valuable reference for policy researchers, corporate sustainability officers, and anyone interested in climate change mitigation.
Key insights from this consolidated data include:
- European countries demonstrate an overall upward trend in carbon prices, with Nordic nations maintaining the highest price levels
- While carbon pricing adoption is expanding in Asia, price levels remain relatively lower compared to European counterparts
- The global average carbon price continues to rise, yet a significant gap remains between current levels and those required to achieve Paris Agreement objectives (50-100 US$/tonCO₂e by 2030)
You can download the three-year carbon pricing data Excel file at no cost via the link below. We hope this resource proves valuable for your research and decision-making processes.
Download Global Carbon Pricing Data 2022-2024
Conclusion
Carbon pricing has emerged as an effective climate change response strategy.
While implementation approaches vary according to economic development stages and industrial structures, it is widely recognized as an essential policy instrument for cost-effective greenhouse gas reduction and transition to a low-carbon economy.
Through ongoing monitoring and data-driven analysis, we anticipate an increasingly effective evolution of carbon pricing policies across nations.
Share :
Related Posts

Understanding Scope-Based Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Introduction Carbon neutrality refers to the process of minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and their sources from human activities, while removing already emitted greenhouse gases through methods such as forest absorption or carbon capture utilization and storage (CCUS).
Read More
The Importance of Setting the System Boundary for Life Cycle Assessment
What is Life Cycle Assessment? Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a structured process that comprehensively evaluates the environmental impacts of a product or service by collecting and analyzing all material and energy flows within a defined system boundary.
Read More